After the age of 20, time seems to go by faster than before. As we reach the age of 30, we may unintentionally start noticing hair turning white at the temples, crow’s feet developing around the eyes, and skin gradually losing its luster. Some people will naturally pay more attention to maintenance and anti-aging care, and their skin may look younger. Through this article, you will be aware of the signs of aging skin, and know when it’s best to start anti-aging skincare.
Wrinkles
The first noticeable signs of skin aging are fine lines and wrinkles. The order of correlation between the grade of facial wrinkles and age increase is eye > lower eyelid > upper eyelid > cheek > forehead > mouth area > nasolabial fold > eyebrow.
Loss of Volume
Wrinkles are easy to spot. However, identifying volume loss and facial contours can be a bit difficult. These changes in the face can be subtle, and the following signs may be caused by a loss of skin volume.

Loss of Elasticity and Deep Wrinkles
Dermal components (such as collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid) decrease and degrade with age; as a result, the skin structure is weakened and loses its elasticity, firmness and brightness. When the skin is no longer supported by the collagen supporting structure, the effects of gravity or cutaneous sagging become apparent and the skin tends to sag.

When to Start Anti-aging Skincare?
There is a contradiction between the irreversibility of skin aging and the desire for an eternal young appearance. Throughout history, efforts have been made to understand the truth of skin aging, prevent the aging process, and even reverse the signs of aging.
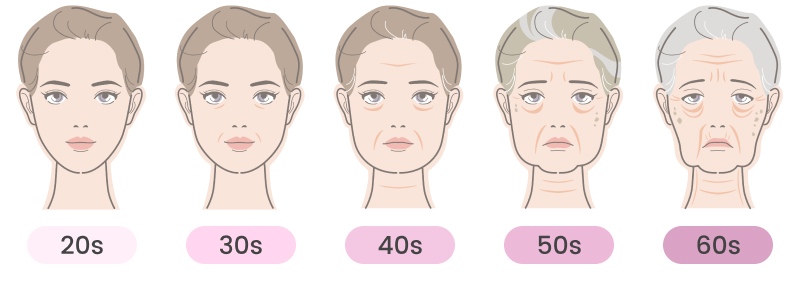
Skincare in Your 20’s
In your 20s, you may think your skin is still perfectly healthy and smooth, but it’s worth noting that, as your skin starts to lose collagen, it starts to lose its grip. At this stage, keeping your skin hydrated and moisturized is key to helping your skin maintain barrier function and keep your skin healthy.
Skincare in Your 30’s
Your 30s are crucial for your skin health. Your skin cell renewal may be affected by environmental aggressors such as UV, pollution, dust, and chemical-laden products, which increase dead cells accumulation on the surface of your skin, leaving your skin looking dull and tired. Hyaluronic acid levels in your skin also naturally drop, meaning your skin loses its natural ability to maintain good hydration levels.
Since the delicate areas around the eyes are often the first to show signs of aging, using serums containing hydrating hyaluronic acid can help reduce the appearance of dark circles and puffiness.
Skincare in Your 40’s
Wrinkles become permanent when your cells can’t recover from damage caused by external aggressors. Your body slows down its production of elastin and collagen, so you need to boost collagen production in your skin. Your skin also tends to be dehydrated in your 40s, and depending on your skin type, you should use more moisturizers with active ingredients daily to keep your skin strong and glowing.
Skincare in Your 50’s +
As you age, your skin becomes thinner, drier and less taut. Not only will wrinkles deepen in the face and neck, but the skin will atrophy as well. Menopause can also wreak havoc on your skin’s shine since your skin loses a lot of collagen and moisture. Applying moisturizing serums, and creams can help eliminate some of the signs of aging.
Voibon Tips
So, When Is The Best Time To Start Using Those Anti-Wrinkle Creams? In short, now. It’s never too late to reach for good skincare. Pay attention to SPF, there’s no point applying the best anti-aging cream and the best anti-aging serum if you don’t also apply SPF, due to the damages the sun can cause the skin.




Acetyl hexapeptide-3(argireline) is used in attempts to decrease the visible effects of aging by reducing the deep wrinkles and lines that occur around the forehead and eyes.
Chemically, when applied as a solution to specific areas of the face, acetyl hexapeptide-3 inhibits the reactions that cause muscles to move or contract – for example when forming facial expressions such as smiling or frowning.