People often say “Asian Don’t Raisin”. But is there anything true about these cliches?
In particular, Asians look much younger in comparison to their true age. Statistical data also shows that Asian ladies enjoy longer lives with better health. For example, China has a low breast cancer rate, and Japan has more than 50,000 people over 100 years.
The first thing that might come to your mind is their diet might influence it. But that is not the case! In this post, we will explore the secret behind this, so keep reading till the end.
Reasons Behind Skin Aging & How are Asians Different
Melanin protects against skin photoaging (wrinkles and discoloration).
Human skin tone ranges from darkest to the palest. These skin colors differ based on the type of pigmentation in the skin, which is known as melanin.
There are two different kinds of melanin; pheomelanin and eumelanin. Like various other skin attributes, skin pigmentation on our skin and its number are determined by our genes.
Scientists have discovered that a couple of genes have a significant role in our skin tone. One of them is melanocortin receptor 1 or MC1R. When it works properly, melanocyte cells can transform pheomelanin into eumelanin. And if it works poorly, pheomelanin starts accumulating.
In people with pale skin, such as Caucasians, this MC1R tends to perform slowly. This is exactly why they have more pheomelanin, resulting in their lighter skin tone.
Moreover, darker skins tend to show aging slowly because it has more melanin in general. So, that darker pigment can determine overall sun sensitivity. And the more melanin you have in your skin, the more safety you have to tackle photoaging.
In general terms, we describe photoaging as having fine lines or cracking in Caucasian skin as it grows old; it’s the cause of overexposure to the sun.
But that doesn’t mean your skin doesn’t age at all just because you are Asian or have a darker skin tone. These attributes can change from ethnicity to ethnicity and person to person.
Another research says that hemoglobin in the dermal-epidermal junction with the papillary dermis is directly associated with skin color. With a proper balance between melanin and hemoglobin, the redness of hemoglobin is concealed by the presence of melanin in different ways.
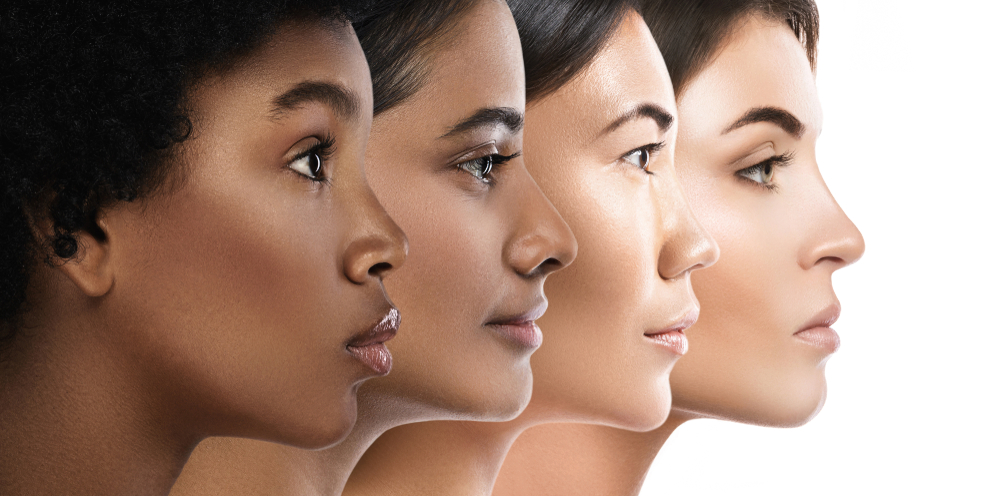

Thicker Dermis Contributes to Reduce Incidence of Wrinkles
Skin aging is directly associated with wrinkles, progressive atrophy of the dermis, and changes in the architectural organization leading to these folds.
Asian skin has compact and thicker dermis than white skin. This thickness is directly proportional to the pigmentation present in the skin. Therefore, it more likely contributes to reduced incidence of facial rhytides in blacks and Asians.
Furthermore, darker skin tones have more cornified layers of cells and lipid content than white skin.
Wider Bone Structure Makes Sagging Less Evident

With aging structural changes occur with fat loss, soft tissue redistribution, and bone resorption. Deep or superficial fat has a more even and consistent distribution in younger people. But with age, fat hypertrophy and atrophy result in irregular contouring.
As a result, sagging appears around the temples, lateral chin, and cheeks. These are gradual changes, but they seem to be more dramatic in white people than Asians.
Asians have different facial structures compared to Caucasians. For example, Asians have a wider bone structure compared to Caucasians. With age, soft tissue loss is less evident due to the wider structure, especially in the middle of the face, including the cheeks, lower eye border, and right above the jawline.
This is the place that comprises most of the volume of a face. These are also the regions where most people go for fillers. But that means Asian skin doesn’t show any signs of aging.
If this skin type has more pigmentation, it will be less likely to raisin but will still show the signs of photodamage. Due to photoaging, black people also have to deal with discoloration or dark spots.
Lifestyle & Diet
Another secret is hidden in the diet of these Asians, and it somewhat also contributes to how they age slowly. You might see a lot of Chinese and Japanese restaurants with different meat-centered dishes. But most Asians don’t have a meat-centered diet. For a very long time, their diet has been primarily vegetarian. The energy from this type of diet lasts longer.
They maintain a healthy work and life balance which keeps them more focused on their work at the right time.
According to the research, the Chinese diet has 20 percent fewer animal foods than the American diet. As a result, they have more antioxidants and other plant-based nutrients such as phytochemicals. These also contribute to the overall healthier way of eating.
You must fill your plate with complex carbs like vegetables and rice instead of meat. Meat should only be used as a flavoring for these healthier alternatives. And the best part is you can only incorporate these items into your daily meal no matter where you are.

VOIBON TIPS
You must protect your skin from the sun every day and follow this routine meticulously. You can also apply a self-tanner instead of getting a tan. Stop smoking and drinking alcohol if you do, and don’t make repetitive facial expressions. Make sure you eat a healthy and balanced diet, followed by a regular workout and proper care of your skin.
Conclusion
Asians age slowly because they have a different skin type that produces more pheomelanin than white skin. Moreover, darker skin tones have more pigmentation, making them less prone to wrinkles.
Asians eat a less meat-centric diet, another contributing factor. You have to make sure you take care of your skin and protect it daily from the sun. It will halt photoaging in the long run. Also, stop smoking and drinking and take care of your skin.
Developing these good habits will ensure you will be able to reduce the effects of skin aging in the long run. It will allow you to look much younger with brighter and glowing skin.